Unpacking Pandora from Its Box: Deciphering the Molecular Basis of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Phylogenetic Profiling of the Novel Coronavirus
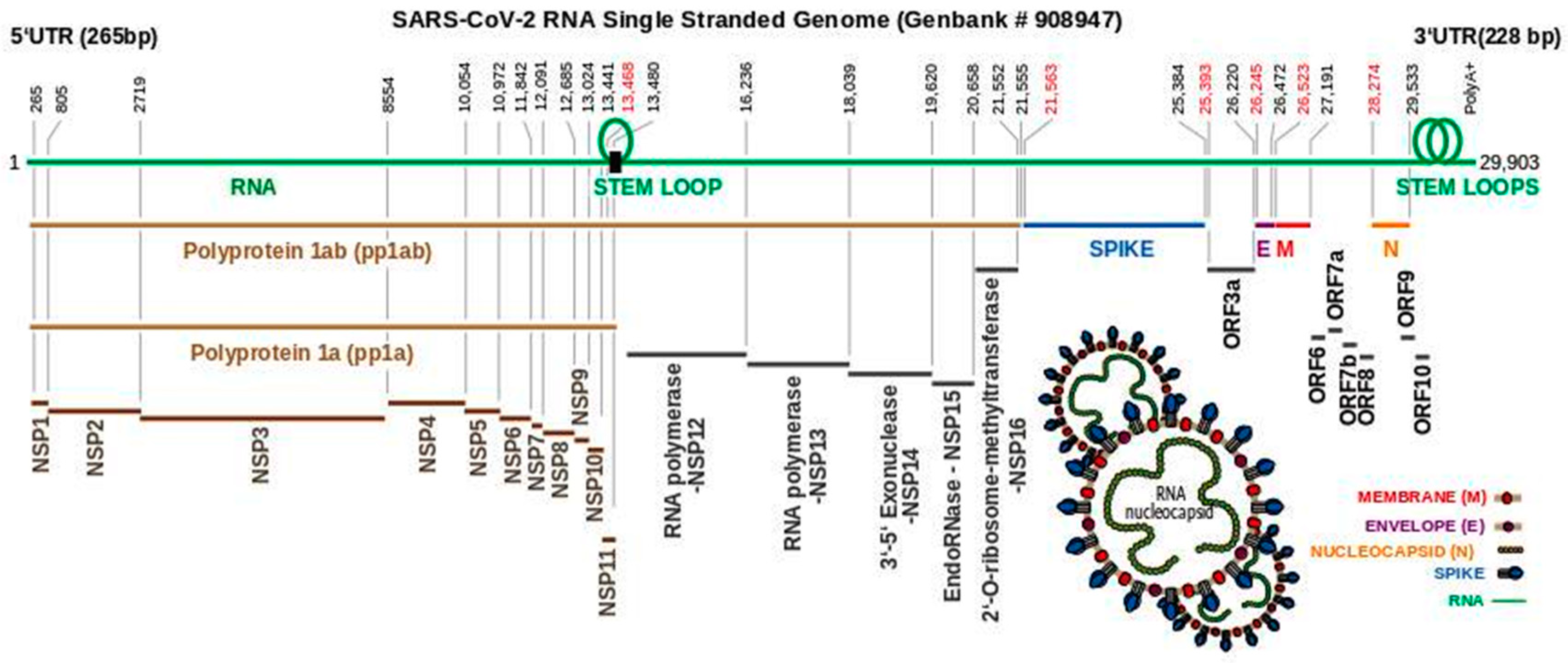
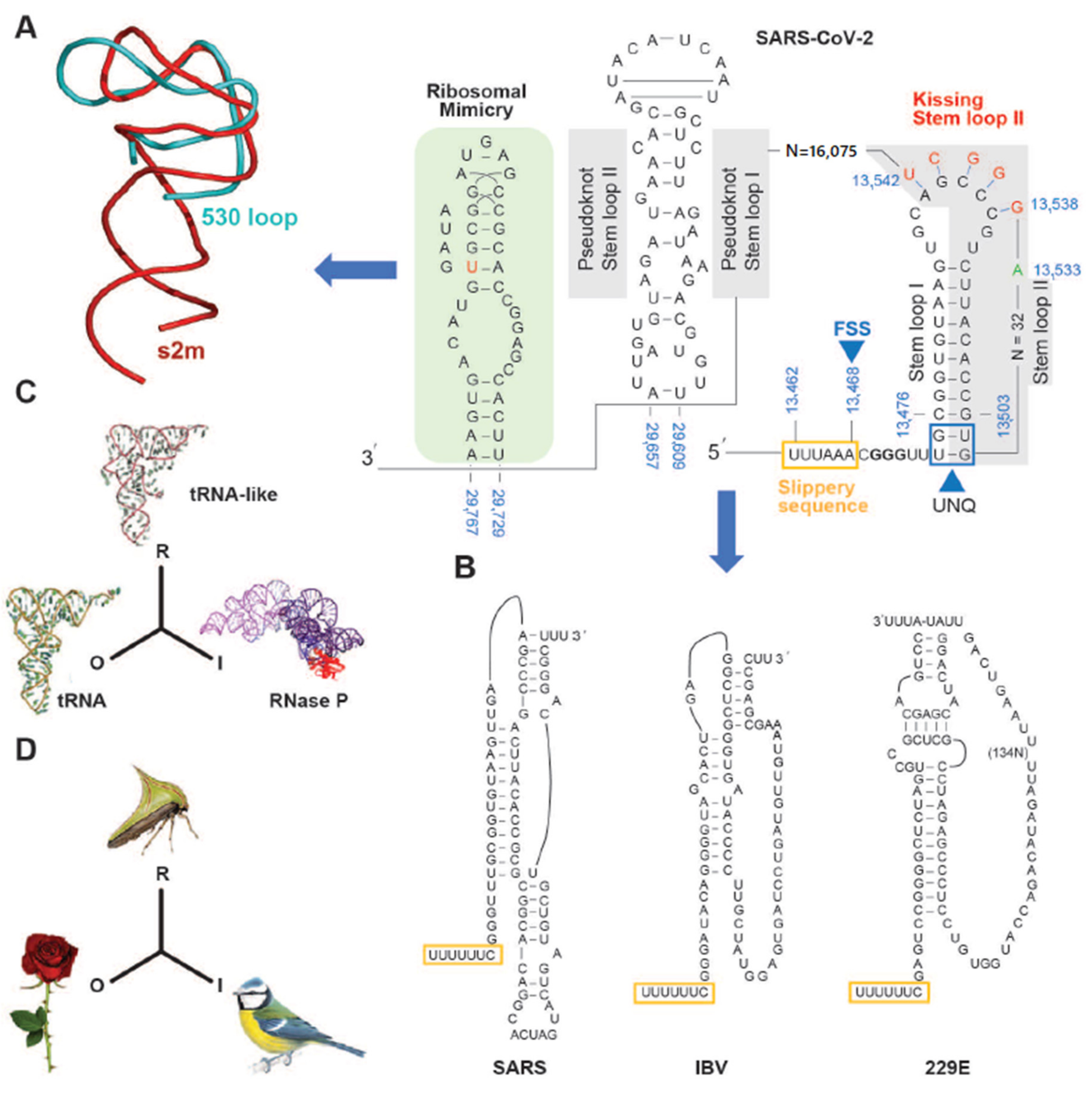
3. The SARS-CoV-2 Genome Throws Up Unique Features in Stem-Loops
4. Polyproteins Translated From the SARS-CoV-2 Genome
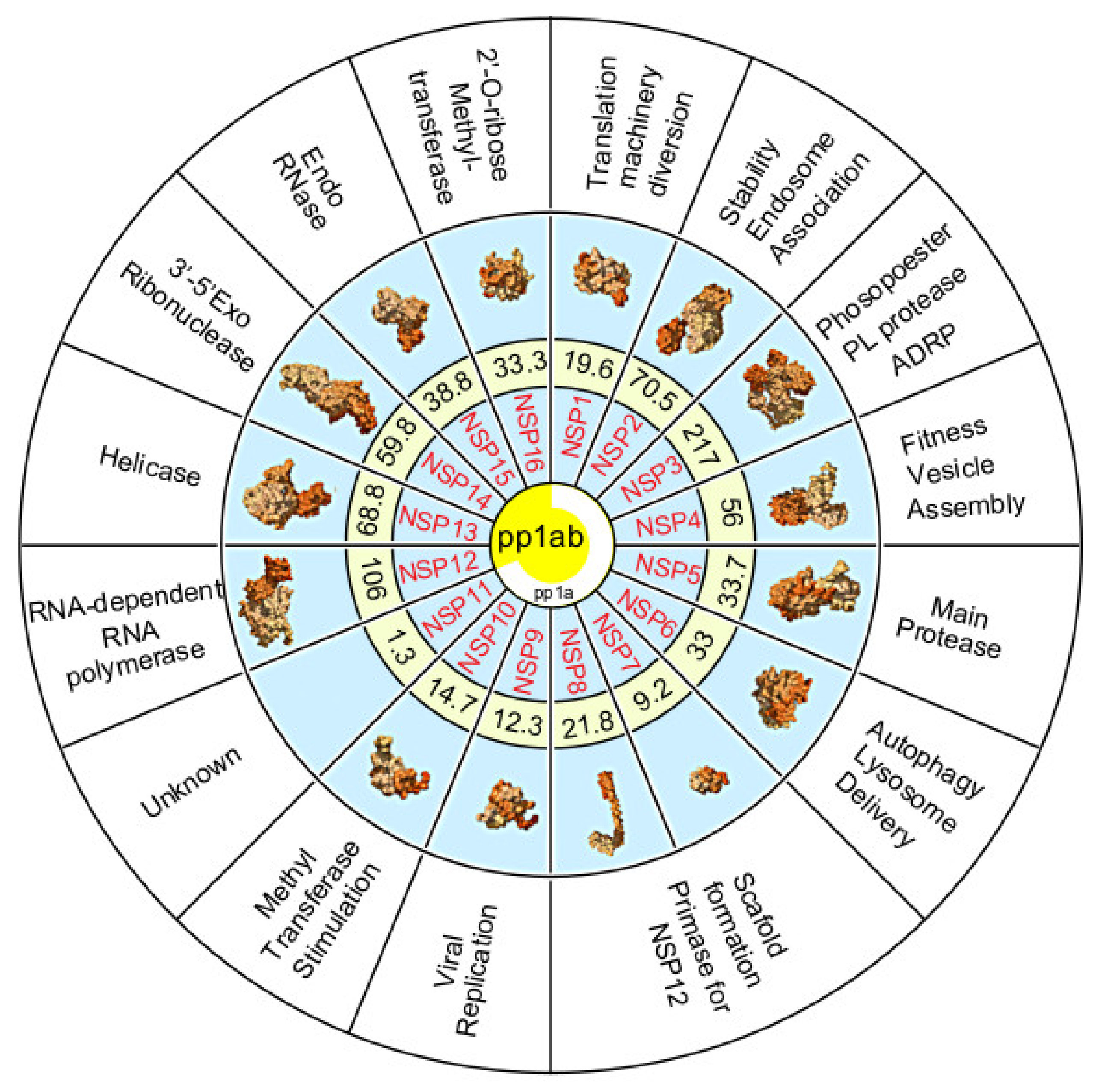
5. The Non-Structural Proteins Encoded by the SARS-CoV-2 Genome
6. SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins
7. Future Mitigation Plans
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gates, B. [Video File]. Ted Talk2015 The Next Outbreak? We’re Not Ready. Available online: https://www.ted.com/talks/bill_gates_the_next_outbreak_we_re_not_ready?language=dz (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Commission WMH. Report of Clustering Pneumonia of Unknown Etiology in Wuhan City; Commission WMH: Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality, and their association with country healthcare resources and economic status. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of V. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Feng, C.L.; Xian, X.Y.; Qiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Q.X.; Kong, S.F.; Chen, Y.C.; Pan, J.P. Novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) CT distribution and sign features. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 2020, 43, E030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas-Conejo, Y.; Linan-Rico, A.; Garcia-Rodriguez, D.A.; Centeno-Leija, S.; Serrano-Posada, H. An exclusive 42 amino acid signature in pp1ab protein provides insights into the evolutive history of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.-M.; Tsoi, H.; Chan, W.-M.; Zhai, S.; Wong, C.-O.; Yao, X.; Chan, W.Y.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Chan, H.Y.E. The ion channel activity of the SARS-coronavirus 3a protein is linked to its pro-apoptotic function. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 Transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, K.B.; Nagy, P.D. Defective Interfering RNAs: Foes of Viruses and Friends of Virologists. Viruses 2009, 1, 895–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.P.; Igel, H.; Baertsch, R.; Haussler, D.; Ares, M.; Scott, W.G. The Structure of a Rigorously Conserved RNA Element within the SARS Virus Genome. PLoS Biol. 2004, 3, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, P.V.; Henderson, C.M.; Anderson, C.B.; Gesteland, R.F.; Atkins, J.F.; Howard, M.T. Programmed ribosomal frameshifting in decoding the SARS-CoV genome. Virology 2005, 332, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketteler, R. On programmed ribosomal frameshifting: The alternative proteomes. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacks, T.; Power, M.D.; Masiarz, F.R.; Luciw, P.A.; Barr, P.J.; Varmus, H.E. Characterization of ribosomal frameshifting in HIV-1 gag-pol expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 1988, 331, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagger, B.W.; Wise, H.M.; Kash, J.C.; Walters, K.-A.; Wills, N.M.; Xiao, Y.-L.; Dunfee, R.L.; Schwartzman, L.M.; Ozinsky, A.; Bell, G.L.; et al. An Overlapping Protein-Coding Region in Influenza A Virus Segment 3 Modulates the Host Response. Science 2012, 337, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, J.; Siddell, S.G. An ‘elaborated’ pseudoknot is required for high frequency frameshifting during translation of HCV 229E polymerase mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 5838–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, I.; Rolley, N.J.; Jenner, A.J.; Inglis, S.C. Mutational analysis of the RNA pseudoknot component of a coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 220, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, I.; Jenner, A.J.; Inglis, S.C. Mutational analysis of the “slippery-sequence” component of a coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 227, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liphardt, J.; Napthine, S.; Kontos, H.; Brierley, I. Evidence for an RNA pseudoknot loop-helix interaction essential for efficient −1 ribosomal frameshifting. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 288, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, C.M.; OJonassen, T.; Grinde, B. A common RNA motif in the 3′ end of the genomes of astroviruses, avian infectious bronchitis virus and an equine rhinovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, T. Mimicry and Meaning: Structure and Semiosis of Biological Mimicry; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ariza-Mateos, A.; Gómez, J. Viral tRNA Mimicry from a Biocommunicative Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Peng, R.; Yuan, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Structural and Biochemical Characterization of the nsp12-nsp7-nsp8 Core Polymerase Complex from SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, E.P.; Pérez-Alvarado, G.C.; Jacobs, J.L.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Hennig, M.; Dinman, J.D. A Three-Stemmed mRNA Pseudoknot in the SARS Coronavirus Frameshift Signal. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, I.; Digard, P.; Inglis, S.C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: Requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell 1989, 57, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilstrup, M. Naturalizing semiotics: The triadic sign of Charles Sanders Peirce as a systems property. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2015, 119, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, A.; Tuller, T. Determinants of Translation Elongation Speed and Ribosomal Profiling Biases in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yao, L.; Wei, T.; Tian, F.; Jin, D.Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, M. Presumed Asymptomatic Carrier Transmission of COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 323, 1406–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, J.; Zimmer, C. Bad News Wrapped in Protein: Inside the Coronavirus Genome. The New York Times, 3 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, K.; Karousis, E.D.; Jomaa, A.; Scaiola, A.; Echeverria, B.; Gurzeler, L.A. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds the ribosomal mRNA channel to inhibit translation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Snyder, G.A.; Giovanetti, M.; Angeletti, S.; Gallo, R.C.; Ciccozzi, M. Emerging of a SARS-CoV-2 viral strain with a deletion in nsp1. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, S.; Benvenuto, D.; Bianchi, M.; Giovanetti, M.; Pascarella, S.; Ciccozzi, M. COVID-2019: The role of the nsp2 and nsp3 in its pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santerre, M.; Arjona, S.P.; Allen, C.N.; Shcherbik, N.; Sawaya, B.E. Why do SARS-CoV-2 NSPs rush to the ER? J. Neurol. 2020, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.T.; Zeb, M.T.; Ahsan, H.; Ahmed, A.; Ali, A.; Akhtar, K. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and Nsp3 binding: An in silico study. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beachboard, D.C.; Anderson-Daniels, J.M.; Denison, M.R. Mutations across Murine Hepatitis Virus nsp4 Alter Virus Fitness and Membrane Modifications. J. Virol. 2014, 89, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemeijer, M.C.; Ulasli, M.; Vonk, A.M.; Reggiori, F.; Rottier, P.J.M.; De Haan, C.A.M. Mobility and Interactions of Coronavirus Nonstructural Protein 4. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4572–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobart, C.C.; Sexton, N.R.; Munjal, H.; Lu, X.; Molland, K.L.; Tomar, S.; Mesecar, A.D.; Denison, M.R. Chimeric Exchange of Coronavirus nsp5 Proteases (3CLpro) Identifies Common and Divergent Regulatory Determinants of Protease Activity. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12611–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xie, W.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Ma, J.; Liang, W. Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors targeting coronavirus main proteases. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e324. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, K.; Ziebuhr, J.; Wadhwani, P.; Mesters, J.R.; Hilgenfeld, R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: Basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science 2003, 300, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, T.; Takemoto, C.; Kim, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Nishii, W.; Terada, T. SARS-CoV 3CL protease cleaves its C-terminal autoprocessing site by novel subsite cooperativity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12997–13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostra, M.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Van Gent, M.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Lintelo, E.G.T.; Rottier, P.J.M.; De Haan, C.A.M. Topology and Membrane Anchoring of the Coronavirus Replication Complex: Not All Hydrophobic Domains of nsp3 and nsp6 Are Membrane Spanning. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12392–12405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falke, S. Coronaviral Polyprotein Nsp7-10: Proteolytic Processing and Dynamic Interactions within the Transcriptase/Replicase Complex. Ph.D. Thesis, Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek, Hamburg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Krichel, B.; Falke, S.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Redecke, L.; Uetrecht, C. Processing of the SARS-CoV pp1a/ab nsp7-10 region. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subissi, L.; Posthuma, C.C.; Collet, A.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Decroly, E.; Snijder, E.J.; Canard, B.; Imbert, I. One severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus protein complex integrates processive RNA polymerase and exonuclease activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3900–E3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littler, D.R.; Gully, B.S. Crystal structure on the SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 9, Nsp9. iScience 2020, 7, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egloff, M.-P.; Ferron, F.; Campanacci, V.; Longhi, S.; Rancurel, C.; Dutartre, H.; Snijder, E.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Cambillau, C.; Canard, B. The severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus replicative protein nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding subunit unique in the RNA virus world. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3792–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, G.; Fry, E.; Carter, L.; Sainsbury, S.; Walter, T.; Nettleship, J. The nsp9 replicase protein of SARS-coronavirus, structure and functional insights. Structure 2004, 12, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miknis, Z.J.; Donaldson, E.F.; Umland, T.C.; Rimmer, R.A.; Baric, R.S.; Schultz, L.W. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus nsp9 Dimerization Is Essential for Efficient Viral Growth. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, V.; Sharma, P.P.; Raj, S.; Choudhari, R.; Rathi, B.; Kesari, K.K. Structure-based drug repurposing for targeting Nsp9 replicase and spike proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, M.; Debarnot, C.; Imbert, I.; Selisko, B.; Snijder, E.J.; Canard, B. In vitro reconstitution of SARS-coronavirus mRNA cap methylation. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugari, A.; Betzi, S.; Decroly, E.; Bonnaud, E.; Hermant, A.; Guillemot, J.-C.; Debarnot, C.; Borg, J.-P.; Bouvet, M.; Canard, B.; et al. Molecular Mapping of the RNA Cap 2′-O-Methyltransferase Activation Interface between Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus nsp10 and nsp16. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33230–33241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, M.; Imbert, I.; Subissi, L.; Gluais, L.; Canard, B.; Decroly, E. RNA 3′-end mismatch excision by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp10/nsp14 exoribonuclease complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9372–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, J.A.; Singh, J.; Singh, H.; Jamal, S.; Khubaib, M.; Kohli, S. Emerging genetic diversity among clinical isolates of SARS-CoV-2: Lessons for today. Infect Genet Evol. 2020, 84, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.L.; Andres, E.L.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Sheahan, T.P.; Lu, X.; Smith, E.C.; Case, J.B.; Feng, J.Y.; Jordan, R.; et al. Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease. mBio 2018, 9, e00221-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.U.; Froeyen, M. Structural elucidation of SARS-CoV-2 vital proteins: Computational methods reveal potential drug candidates against main protease, Nsp12 polymerase and Nsp13 helicase. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neogi, U.; Hill, K.J.; Ambikan, A.T.; Heng, X.; Quinn, T.P.; Byrareddy, S.N. Feasibility of Known RNA Polymerase Inhibitors as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drugs. Pathogens 2020, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, A.; Le, N.T.; Selisko, B.; Eydoux, C.; Alvarez, K.; Guillemot, J.C. Remdesivir and SARS-CoV-2: Structural requirements at both nsp12 RdRp and nsp14 Exonuclease active-sites. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieman, M.; Basu, D.; Matthews, K.; Taylor, J.; Jones, G.; Pickles, R. Yeast based small molecule screen for inhibitors of SARS-CoV. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.K.; Shakya, A.; Prasad, S.K.; Singh, S.; Gurav, N.S.; Prasad, R.S. An in-silico evaluation of different Saikosaponins for their potency against SARS-CoV-2 using NSP15 and fusion spike glycoprotein as targets. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, A.; Xu, S.; Pan, R.; Zeng, C. Coronavirus nsp10/nsp16 Methyltransferase Can Be Targeted by nsp10-Derived Peptide In Vitro and In Vivo To Reduce Replication and Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8416–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, E.; Merhi, G.; Panossian, B.; Salloum, T.; Tokajian, S. SARS-CoV-2 and ORF3a: Nonsynonymous Mutations, Functional Domains, and Viral Pathogenesis. mSystems 2020, 5, e00266–e00320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieman, M.; Yount, B.; Heise, M.; Kopecky-Bromberg, S.A.; Palese, P.; Baric, R. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF6 Antagonizes STAT1 Function by Sequestering Nuclear Import Factors on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum/Golgi Membrane. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9812–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.K.; Coleman, C.M.; Postel, S.; Sisk, J.M.; Bernbaum, J.G.; Venkataraman, T.; Sundberg, E.J.; Frieman, M.B. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF7a Inhibits Bone Marrow Stromal Antigen 2 Virion Tethering through a Novel Mechanism of Glycosylation Interference. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11820–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, L.A.; Kaelin, E.A.; Maqsood, R.; Estifanos, B.; Wu, L.I.; Varsani, A. An 81 nucleotide deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a identified from sentinel surveillance in Arizona (Jan-Mar 2020). J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00711–e00720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekosz, A.; Schaecher, S.R.; Diamond, M.S.; Fremont, D.H.; Sims, A.C.; Baric, R.S. Structure, expression, and intracellular localization of the SARS-CoV accessory proteins 7a and 7b. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 581, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oostra, M.; De Haan, C.A.M.; Rottier, P.J.M. The 29-Nucleotide Deletion Present in Human but Not in Animal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses Disrupts the Functional Expression of Open Reading Frame 8. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13876–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagliani, R.; Forni, D.; Clerici, M.; Sironi, M. Computational Inference of Selection Underlying the Evolution of the Novel Coronavirus, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.; Kok, K.-H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.-W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.J. Virus Taxonomy. In Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Press, E.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 806–828. [Google Scholar]
- Konrad, R.; Eberle, U.; Dangel, A.; Treis, B.; Berger, A.; Bengs, K. Rapid establishment of laboratory diagnostics for the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in Bavaria, Germany, February 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. Structure, Function, and Evolution of Coronavirus Spike Proteins. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankadari, N.; Wilce, J.A. Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Shang, J.; Graham, R.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Receptor Recognition by the Novel Coronavirus from Wuhan: An Analysis Based on Decade-Long Structural Studies of SARS Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutard, B.; Valle, C.; De Lamballerie, X.; Canard, B.; Seidah, N.; Decroly, E. The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furin-like cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade. Antivir. Res. 2020, 176, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korber, B.; Fischer, W.M.; Gnanakaran, S.; Yoon, H.; Theiler, J.; Abfalterer, W. Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus. Cell 2020, 182, 812–827.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Loman, N.; Pybus, O.; Barclay, W.; Barrett, J.; Carabelli, A. Preliminary genomic characterisation of an emergent SARS-CoV-2 lineage in the UK defined by a novel set of spike mutations. Genom. Epidemiol. 2020. Available online: https://virological.org/t/preliminary-genomic-characterisation-of-an-emergent-sars-cov-2-lineage-in-the-uk-defined-by-a-novel-set-of-spike-mutations/563 (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Kandeel, M.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Fayez, M.; Al-Nazawi, M. From SARS and MERS CoVs to SARS-CoV-2: Moving toward more biased codon usage in viral structural and nonstructural genes. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruch, T.R.; Machamer, C.E. The Coronavirus E Protein: Assembly and Beyond. Viruses 2012, 4, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.K.-M.; Dunker, A.K.; Foster, J.A.; Uversky, V. HIV Vaccine Mystery and Viral Shell Disorder. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralinski, L.E.; Menachery, V.D. Return of the Coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Graham, R.L.; Baric, R. Jumping species—A mechanism for coronavirus persistence and survival. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.; Van Zyl, M.; Fielding, B.C. The Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Is a Multifunctional Protein. Viruses 2014, 6, 2991–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechetkin, V.R.; Lobzin, V.V. Ribonucleocapsid assembly/packaging signals in the genomes of the coronaviruses SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2: Detection, comparison and implications for therapeutic targeting. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Cui, H.; Gao, Z.; Liu, M.; Lu, S.; Mkandawire, W. Structural Genomics of SARS-CoV-2 Indicates Evolutionary Conserved Functional Regions of Viral Proteins. Viruses 2020, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikatendu, K.S.; Joseph, J.S.; Subramanian, V.; Clayton, T.; Griffith, M.; Moy, K.; Velasquez, J.; Neuman, B.W.; Buchmeier, M.J.; Stevens, R.C.; et al. Structural Basis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ADP-Ribose-1″-Phosphate Dephosphorylation by a Conserved Domain of nsP3. Structure 2005, 13, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Leary, V.B.; Dolly, O.J.; Höschl, C.; Černa, M.; Ovsepian, S.V. Unpacking Pandora from Its Box: Deciphering the Molecular Basis of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010386
O’Leary VB, Dolly OJ, Höschl C, Černa M, Ovsepian SV. Unpacking Pandora from Its Box: Deciphering the Molecular Basis of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010386
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Leary, Valerie Bríd, Oliver James Dolly, Cyril Höschl, Marie Černa, and Saak Victor Ovsepian. 2021. "Unpacking Pandora from Its Box: Deciphering the Molecular Basis of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010386
APA StyleO’Leary, V. B., Dolly, O. J., Höschl, C., Černa, M., & Ovsepian, S. V. (2021). Unpacking Pandora from Its Box: Deciphering the Molecular Basis of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010386






